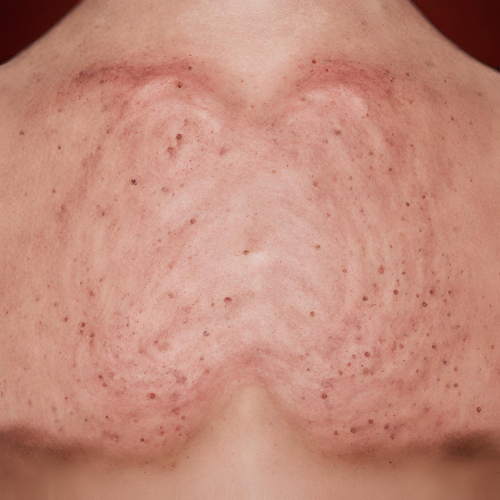
Exploring Folliculitis: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Management
What is Folliculitis? Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles, the tiny pockets in the skin from which hair grows. It can occur anywhere on the body where hair follicles are present and may present as small red bumps, pus-filled lesions, or pustules around hair follicles. Folliculitis can be acute or chronic and may result from bacterial, fungal, viral, or parasitic infections, as well as non-infectious causes.
Symptoms of Folliculitis:
- Red or inflamed skin around hair follicles.
- Small, pus-filled bumps or pustules.
- Itchy or tender skin.
- Pain or discomfort in affected areas.
- Crusting or scabbing over affected follicles.
- Occasionally, hair loss in severe cases.
Causes and Risk Factors: Folliculitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Bacterial infections (most commonly Staphylococcus aureus).
- Fungal infections (such as yeast or dermatophyte fungi).
- Viral infections (e.g., herpes simplex virus).
- Parasitic infections (e.g., scabies or demodex mites).
- Irritation from shaving, friction, or certain skincare products.
- Blockage of hair follicles due to oils, sweat, or debris.
- Compromised immune system.
- Hot tub folliculitis (Pseudomonas folliculitis) from contaminated water.
Diagnosis: Diagnosing folliculitis typically involves a visual examination of the affected skin and may require additional tests, such as:
- Microscopic examination: A sample of the affected skin may be examined under a microscope to identify the presence of bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms.
- Culture test: A swab or scraping of the affected skin may be sent to a laboratory for culture to determine the specific type of microorganism causing the infection.
- Skin biopsy: In rare or severe cases, a small sample of skin tissue may be removed and examined under a microscope to rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment Options: Treatment for folliculitis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common treatment approaches may include:
- Topical antibiotics: Antibacterial creams or ointments may be prescribed to treat bacterial folliculitis.
- Antifungal medications: For fungal folliculitis, antifungal creams, lotions, or oral medications may be recommended.
- Antiviral drugs: Oral antiviral medications may be prescribed for folliculitis caused by herpes simplex virus.
- Warm compresses: Applying warm compresses to affected areas can help reduce inflammation and promote drainage of pus.
- Proper hygiene: Good hygiene practices, such as keeping the skin clean and dry and avoiding tight clothing, can help prevent folliculitis and promote healing.
- Avoidance of irritants: Identifying and avoiding potential triggers, such as harsh skincare products or tight clothing, can help prevent recurrent folliculitis.
Management and Prevention: In addition to treatment, certain measures can help manage folliculitis and reduce the risk of recurrence:
- Avoid shaving over affected areas until the condition improves.
- Use gentle skincare products and avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive exfoliants.
- Keep skin clean and dry, especially after sweating or swimming.
- Wash clothing, towels, and bedding regularly to prevent the spread of infection.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as razors, towels, or clothing with others.
- Seek prompt medical attention if folliculitis symptoms worsen or do not improve with home care measures.
Conclusion: Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation of hair follicles, often resulting in red bumps, pustules, or pus-filled lesions. While it can be uncomfortable and unsightly, most cases of folliculitis are self-limiting and respond well to treatment. By identifying the underlying cause and adopting appropriate management strategies, individuals can effectively manage folliculitis and reduce the risk of recurrence. However, persistent or severe cases of folliculitis may require medical intervention, including prescription medications or procedures. If you suspect you have folliculitis or have concerns about your skin health, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.